| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | APCC-binding Destruction motifs |
| Functional site description: | The anaphase-promoting ubiquitin ligase complex APC/C selectively targets numerous cell cycle-regulatory proteins for ubiquitin-mediated proteasome-dependent degradation. The targets of the APC/C are degraded in an ordered, sequential manner which ensures the correct progression of the cell cycle. Cdh1 and Cdc20 are WD-repeat containing proteins which act as co-activators of the APC/C at distinct steps of the cycle. Cdc20 joins the APC/C in early mitosis and is then replaced by Cdh1 during anaphase. Both Cdh1 and Cdc20 recognize the target proteins via short, very specific "destruction motifs". The motifs allow recruitment of the targets, to the APC/C complex which subsequently poly-ubiquitinates them. |
| ELMs with same func. site: | DEG_APCC_DBOX_1 DEG_APCC_KENBOX_2 |
| ELM Description: | The KEN Box is a short sequence motif, comprising a highly conserved KEN sequence. It is found in several key cell cycle proteins where it acts as a signal for cycle-dependent proteolysis. The first KEN box (consensus KEN) was identified within Cdc20 (Pfleger,2000). Later, active KEN boxes were also found within human CDC6, securin, Drosophila cyclin A, yeast Hsl1, Clb2, Aurora kinase B, BUB1 and CIN8 (see references). The KEN-box is preferentially recognised by the APC/C coactivator Cdh1, which subsequently recruits the APC/C E3 ubiquitin ligase complex, leading to the ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of the target protein. Cdh1- mediated protein degradation of KEN-box containing proteins is focused in the late mitosis and early G1 phase of the cell cycle. |
| Pattern: | .KEN. |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0001843 |
| Present in taxon: | Eukaryota |
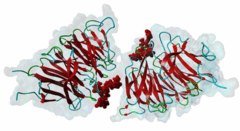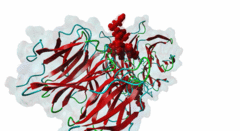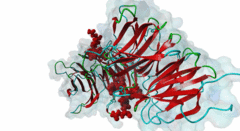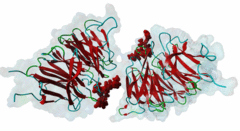
| Interaction Domain: |
WD40 (PF00400)
WD domain, G-beta repeat
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
Progress of cell division is governed by the sequential degradation, mediated by the ubiquitination pathway, of proteins playing a key role in the cell cycle. There are two E3 ubiquitin protein ligase complexes which play a role in the cell cycle: the SCF (Skp1/Cullin/F-box) complex and the anaphase-promoting complex (APC/C) (Peters,2006, Castro,2005). The APC/C complex contains at least a dozen different subunits, but it can ubiquitylate substrates only in the presence of the co-activator proteins Cdc20 (also known as fizzy) or Cdh1(also called fzr or Hct1). Cdh1 and Cdc20 are WD40-repeat proteins (well known linear motif-binding domains, folded as 7-blade beta-propellers), which recognise their target proteins via short "degradation motifs". Cdc20 and Cdh1 act at distinct phases of the cell cycle. Early in mitosis, during the metaphase-anaphase transition, APC/Cdc20 is mostly active, whereas Cdh1 is present, but as a phosphorylated inactive form which cannot bind to the APC/C. Later, in mitotic exit and further during the G1 phases, Cdh1 is activated by dephosphorylation, and binds to the APC/C by replacing Cdc20 and promoting its rapid degradation. A number of degradation motifs have been identified within APC/C substrate proteins. These motifs are generally defined as short conserved sequences whose deletion or mutation promotes the stabilisation of the proteins where they are naturally found, and which can confer cell-cycle dependent degradation on unrelated proteins. The best characterised ones are the Destruction box (D-box) and KEN box. The D-box was originally found in the cyclin B protein to be necessary to induce cyclin B degradation (Glotzer,1991). Moreover, when fused to a foreign protein it is sufficient to generate a cycle-dependent proteolytic pattern similar to that observed for cyclin B. It is one of the earlier described linear motifs. Its short sequence is usually represented as a highly conserved RxxL motif, however the ELM annotators consider that the conservation is better described by the motif RxxLxx[LIVM]. Subsequent studies demonstrated a D-box-dependent degradation of other key cell-cycle players such as cyclin A (Glotzer,1991), geminin (McGarry,1998), securin (Zou,1999) and Plk1 (Lindon,2004), all of which strictly obey the extended motif. Proposed D-boxes in Cdc6 and Nek2 do not match the extended motif while the motifs proposed in Aurora A and Aurora B are deeply buried in the kinase domain. Indeed, Nguyen,2005 were not able to reproduce D-box function in Aurora B. It is of note that the problematic D-box proteins all have highly conserved KEN boxes. The first KEN box (consensus KEN) was identified within Cdc20 itself (Pfleger,2000). Later, active KEN boxes were also reported within human CDC6, securin, Drosophila cyclin A, yeast Hsl1, Clb2, Aurora kinase B, BUB1 and CIN8 (see attached references). Candidate KEN boxes (without experimental verification) have been proposed in many other proteins including HipK2, Eg5, DNA Topo1 and Cdc27 (Michael,2008). Both D-box and KEN-box are recognised by Cdh1 and/or Cdc20, which subsequently recruit the APC/C complex, leading to the ubiquitination and proteasome-mediated degradation of the target protein. The D-box is recognized by both Cdc20 and Cdh1, whereas the KEN-box is preferentially recognized by Cdh1. Cdc20 itself contains a KEN box, which is therefore recognized by Cdh1, ensuring the temporal degradation of Cdc20 and its replacement by Cdh1 as a cofactor of the APC/C. Experimental studies of APC-target proteins have shown that some of them contain only D-box, others contain only KEN-box, some contain both. D-box and KEN can act as an independent entity or as a co-ordinate unit for protein degradation. The presence of D-box or KEN-box motifs in a sequence does not always guarantee that they are active degradation signals for the proteins in which they are found. Indeed, there is always a possibility that the protein in which a potential destruction motif has been mutated becomes resistant to proteasome degradation due to serious misfolding and aggregation, and not because of losing a specific APC/C-targeting site. Putative destruction motifs found within areas predicted to be natively disordered are much more likely to be active than those found in known or predicted globular regions/domains. |
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement