| Accession: | |
|---|---|
| Functional site class: | SxIP motif |
| Functional site description: | End binding homology (EBH) domains recognize SxIP motifs embedded within basic and Pro/Ser rich sequence regions of microtubule plus-end tracking proteins (+TIPs). The EBH-SxIP interaction is used by numerous +TIPs to target end binding (EB) proteins at growing microtubule ends. |
| ELM Description: | SxIP motifs within basic and Pro/Ser rich sequence regions bind to EBH domains of EB proteins. Both, the SxIP sequence as well as basic, not strictly conserved, residues in the vicinity of the motif site contribute to the EBH-SxIP binding affinity. Some SxIP motifs are known to be regulated by phosphorylation while acidic residues are strongly disfavoured in the local regions. The current regular expression partially captures this context. There must be either no negative charge within 5 residues or else a basic residue closer to the SxIP than an acidic residue. All SxIP motifs reported by Honnappa,2009 are detected by the pattern. There is one report of a functional SxLP motif in a strongly basic sequence context (Fong,2009). For the moment, the ELM pattern excludes Leu until binding affinities and sequence context of SxLP motifs are better described. Difficult to predict SxIP in entire Proteomes. Possible to predict in proteins known to bind directly to EBs and associated with microtubules. |
| Pattern: | ([KR][^ED]{0,5}[ST].IP[^ED]{5,5})|([^ED]{5,5}[ST].IP[^ED]{0,5}[KR]) |
| Pattern Probability: | 0.0002096 |
| Present in taxon: | Eukaryota |
| Interaction Domain: |
EB1 (PF03271)
EB1-like C-terminal motif
(Stochiometry: 1 : 1)
|
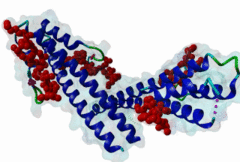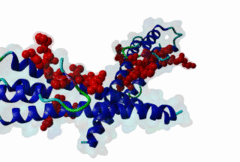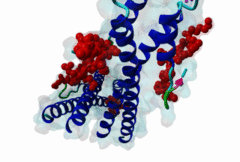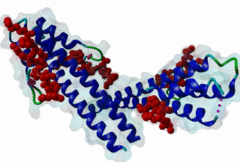
The end binding homology (EBH) domain (PF03271) is a small, approximately 50-residue protein module highly conserved in organisms from yeast to man. It is exclusively found in end binding (EB) proteins. EB proteins autonomously track growing microtubule plus ends and act as a hub within dynamic microtubule plus-end tracking protein (+TIP) networks. +TIPs constitute a diverse group of evolutionarily conserved microtubule-associated proteins that specifically accumulate at the ends of growing microtubules. They play important roles in essential cellular activities, including chromosome segregation, cell polarization and migration, organelle transport, and intracellular signalling. The C-terminal EBH domain of EB proteins binds to an array of structurally and functionally unrelated +TIP binding partners, including the adenomatous polyposis coli (APC) tumor suppressor protein, the microtubule-actin crosslinking factor (MACF), the cytoplasmic linker protein (CLIP170), CLIP-associated proteins (CLASPs), the transmembrane protein stromal interaction molecule-1 (STIM1), the dynactin large subunit p150glued, and the mitotic centromere-associated kinesin (MCAK). SxIP motifs embedded within basic and Pro/Ser rich sequence regions of numerous +TIPs specifically bind to highly conserved residues shaping a hydrophobic groove in the EBH domain. Thus EBH domains are SxIP recognition domains. The EBH-SxIP interaction is used to target +TIPs to EBs at growing microtubule ends. Therefore, SxIP motifs act as general microtubule tip localization signals (MtLS). |
(click table headers for sorting; Notes column: =Number of Switches, =Number of Interactions)
| Acc., Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | #Ev. | Organism | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Q6PGN9 PSRC1 PSRC1_HUMAN |
276 | 289 | SSSQLPIPSAIPRPASRMPL | TP | 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| Q91V27 Mlph MELPH_MOUSE |
493 | 506 | PSGKPRRKSGIPIFLPRVTE | TP | 1 | Mus musculus (House mouse) | |
| Q9C0H9 SRCIN1 SRCN1_HUMAN |
1032 | 1046 | SEKPSASRTSIPVLTSFGAR | TP | 1 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| Q99661 KIF2C KIF2C_HUMAN |
93 | 104 | QKQKRRSVNSKIPAPKESLR | TP | 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| Q13586 STIM1 STIM1_HUMAN |
637 | 651 | ALQASRNTRIPHLAGKKAVA | TP | 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| O75122 CLASP2 CLAP2_HUMAN |
515 | 525 | LSVARSSRIPRPSVSQGCSR | TP | 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| O75122 CLASP2 CLAP2_HUMAN |
492 | 502 | ASAQKRSKIPRSQGCSREAS | TP | 4 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| Q03001 DST DYST_HUMAN |
7545 | 7558 | SRPSTAKPSKIPTPQRKSPA | TP | 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) | |
| P25054 APC APC_HUMAN |
2801 | 2811 | STSARPSQIPTPVNNNTKKR | TP | 6 | Homo sapiens (Human) |
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement