| Accession | Acc. Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | PDB | Organism | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELMI001318 | P55211 CASP9 CASP9_HUMAN |
315 | 319 | PGSNPEPDATPFQEGLRTFD | TP |
1NW9  3D9T
3D9T 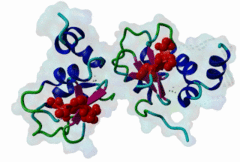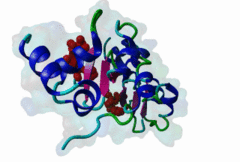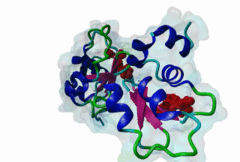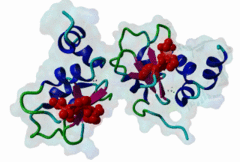
|
Homo sapiens (Human) | 416 |
![]() Instance evidence
Instance evidence
| Evidence class | PSI-MI | Method | BioSource | PubMed | Logic | Reliability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| experimental | MI:0074 | mutation analysis | in vivo/in vitro | Shiozaki,2003 | support | certain | FeatureDetection |
| experimental | MI:0114 | x-ray crystallography | in vitro | Shiozaki,2003 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
| experimental | MI:0114 | x-ray crystallography | in vitro | Kulathila,2009 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
| experimental | MI:0107 | surface plasmon resonance | in vitro | Kulathila,2009 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
![]() Switches
Switches
This ELM instance is part of the following 2 switching mechanisms annotated at the switches.ELM resource:
-
SWTI000527:
Binding of the BIR domain-binding motif of Caspase-9 (CASP9) to the BIR domains of Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 4 (XIAP) requires cleavage of Caspase-9 (CASP9) at D315, since this results in a functional neo N-terminal motif. BIR domains are found in Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs) that suppress the activity of activated caspases, either by directly inhibiting caspase catalytic activity, or by targeting caspases for degradation by ubiquitin modification.
-
SWTI000528:
Binding of the BIR domain-binding motif of Caspase-9 (CASP9) to the BIR domains of Baculoviral IAP repeat-containing protein 2 (BIRC2) requires cleavage of Caspase-9 (CASP9) at D315, since this results in a functional neo N-terminal motif. BIR domains are found in Inhibitor of Apoptosis Proteins (IAPs) that suppress the activity of activated caspases, either by directly inhibiting caspase catalytic activity, or by targeting caspases for degradation by ubiquitin modification.
![]() Pathways
Pathways
- Alzheimer disease
- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
- Apoptosis
- Apoptosis multiple species
- Colorectal cancer
- Endometrial cancer
- Epstein Barr virus infection
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Herpes simplex virus 1 infection
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Huntington disease
- Influenza A
- Kaposi sarcoma associated herpesvirus infection
- Legionellosis
- Lipid and atherosclerosis
- Measles
- Non small cell lung cancer
- PI3K Akt signaling pathway
- Pancreatic cancer
- Parkinson disease
- Pathogenic Escherichia coli infection
- Pathways in cancer
- Pathways of neurodegeneration multiple diseases
- Platinum drug resistance
- Prion disease
- Prostate cancer
- Small cell lung cancer
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Toxoplasmosis
- Tuberculosis
- VEGF signaling pathway
- Viral myocarditis
- p53 signaling pathway
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement


