| Accession | Acc. Gene-, Name | Start | End | Subsequence | Logic | PDB | Organism | Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ELMI003008 | P04049 RAF1 RAF1_HUMAN |
254 | 263 | GSLSQRQRSTSTPNVHMVST | TP |
3IQJ 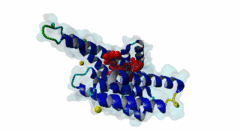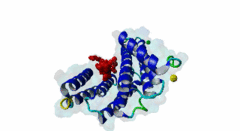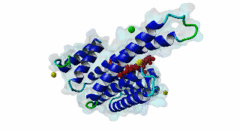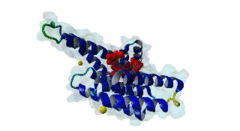 3O8I
3O8I 4IHL |
Homo sapiens (Human) | 648 |
![]() Instance evidence
Instance evidence
| Evidence class | PSI-MI | Method | BioSource | PubMed | Logic | Reliability | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| experimental | MI:0034 | display technology | in vivo/in vitro | Muslin,1996 | support | certain | InteractionDetection |
| experimental | MI:0107 | surface plasmon resonance | in vitro | Muslin,1996 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
| experimental | MI:0053 | fluorescence polarization spectroscopy | in vitro | Molzan,2013 | support | certain | InteractionDetection |
| experimental | MI:0114 | x-ray crystallography | in vitro | Molzan,2013 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
| experimental | MI:0065 | isothermal titration calorimetry | in vitro | Molzan,2010 | support | certain | InteractionDetection |
| experimental | MI:0114 | x-ray crystallography | in vitro | Molzan,2010 | support | certain | InteractionDetection FeatureDetection |
![]() Switches
Switches
This ELM instance is part of the following 2 switching mechanisms annotated at the switches.ELM resource:
-
SWTI000189:
Phosphorylation of S257 in the 14-3-3-binding motif of RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase (RAF1) abolishes binding of the motif, phosphorylated at S259, to 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta (YWHAZ).
-
SWTI000354:
Phosphorylation of two 14-3-3-binding motifs in RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase (RAF1) in response to growth factors induces high-avidity binding to dimeric 14-3-3 protein zeta/delta (YWHAZ), with pS621 being the high-affinity interaction site. This interaction locks RAF proto-oncogene serine/threonine-protein kinase (RAF1) in an inhibited conformation.
![]() Pathways
Pathways
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- Alcoholism
- Alzheimer disease
- Apelin signaling pathway
- Apoptosis
- Autophagy animal
- Axon guidance
- B cell receptor signaling pathway
- Bladder cancer
- Breast cancer
- C type lectin receptor signaling pathway
- Cellular senescence
- Central carbon metabolism in cancer
- Chemical carcinogenesis reactive oxygen species
- Chemical carcinogenesis receptor activation
- Chemokine signaling pathway
- Choline metabolism in cancer
- Chronic myeloid leukemia
- Colorectal cancer
- EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor resistance
- Endocrine resistance
- Endometrial cancer
- ErbB signaling pathway
- Estrogen signaling pathway
- Fc epsilon RI signaling pathway
- Fc gamma R mediated phagocytosis
- Focal adhesion
- FoxO signaling pathway
- Gap junction
- Gastric cancer
- Glioma
- GnRH secretion
- GnRH signaling pathway
- Growth hormone synthesis, secretion and action
- Hepatitis B
- Hepatitis C
- Hepatocellular carcinoma
- Human cytomegalovirus infection
- Human immunodeficiency virus 1 infection
- Human papillomavirus infection
- Influenza A
- Insulin signaling pathway
- JAK STAT signaling pathway
- Kaposi sarcoma associated herpesvirus infection
- Long term depression
- Long term potentiation
- MAPK signaling pathway
- Melanogenesis
- Melanoma
- MicroRNAs in cancer
- Natural killer cell mediated cytotoxicity
- Neurotrophin signaling pathway
- Neutrophil extracellular trap formation
- Non small cell lung cancer
- Oxytocin signaling pathway
- PD L1 expression and PD 1 checkpoint pathway in cancer
- PI3K Akt signaling pathway
- Pancreatic cancer
- Parathyroid hormone synthesis, secretion and action
- Pathways in cancer
- Pathways of neurodegeneration multiple diseases
- Phospholipase D signaling pathway
- Progesterone mediated oocyte maturation
- Prolactin signaling pathway
- Prostate cancer
- Proteoglycans in cancer
- Rap1 signaling pathway
- Ras signaling pathway
- Regulation of actin cytoskeleton
- Relaxin signaling pathway
- Renal cell carcinoma
- Salmonella infection
- Serotonergic synapse
- Signaling pathways regulating pluripotency of stem cells
- Sphingolipid signaling pathway
- T cell receptor signaling pathway
- Thyroid hormone signaling pathway
- Tuberculosis
- VEGF signaling pathway
- Vascular smooth muscle contraction
- cAMP signaling pathway
- cGMP PKG signaling pathway
- mTOR signaling pathway
Please cite:
ELM-the Eukaryotic Linear Motif resource-2024 update.
(PMID:37962385)
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement
ELM data can be downloaded & distributed for non-commercial use according to the ELM Software License Agreement


